Boogeyman 1
A new threat actor emerges from the wild using the name Boogeyman. Are you afraid of the Boogeyman?
[Introduction] New threat in town.
Start Machine
Uncover the secrets of the new emerging threat, the Boogeyman.
In this room, you will be tasked to analyse the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) executed by a threat group, from obtaining initial access until achieving its objective.

Prerequisites
This room may require the combined knowledge gained from the SOC L1 Pathway. We recommend going through the following rooms before attempting this challenge.
Tshark (coming soon!)
Investigation Platform
Before we proceed, deploy the attached machine by clicking the Start Machine button in the upper-right-hand corner of the task. It may take up to 3-5 minutes to initialise the services.
The machine will start in a split-screen view. In case the VM is not visible, use the blue Show Split View button at the top-right of the page.
Artefacts
For the investigation proper, you will be provided with the following artefacts:
Copy of the phishing email (dump.eml)
Powershell Logs from Julianne's workstation (powershell.json)
Packet capture from the same workstation (capture.pcapng)
Note: The powershell.json file contains JSON-formatted PowerShell logs extracted from its original evtx file via the evtx2json tool.
You may find these files in the /home/ubuntu/Desktop/artefacts directory.
Tools
The provided VM contains the following tools at your disposal:
Thunderbird - a free and open-source cross-platform email client.
LNKParse3 - a python package for forensics of a binary file with LNK extension.
Wireshark - GUI-based packet analyser.
Tshark - CLI-based Wireshark.
jq - a lightweight and flexible command-line JSON processor.
To effectively parse and analyse the provided artefacts, you may also utilise built-in command-line tools such as:
grep
sed
awk
base64
Now, let's start hunting the Boogeyman!
Answer the questions below
Let's hunt that boogeyman!
Completed
[Email Analysis] Look at that headers!
The Boogeyman is here!
Julianne, a finance employee working for Quick Logistics LLC, received a follow-up email regarding an unpaid invoice from their business partner, B Packaging Inc. Unbeknownst to her, the attached document was malicious and compromised her workstation.
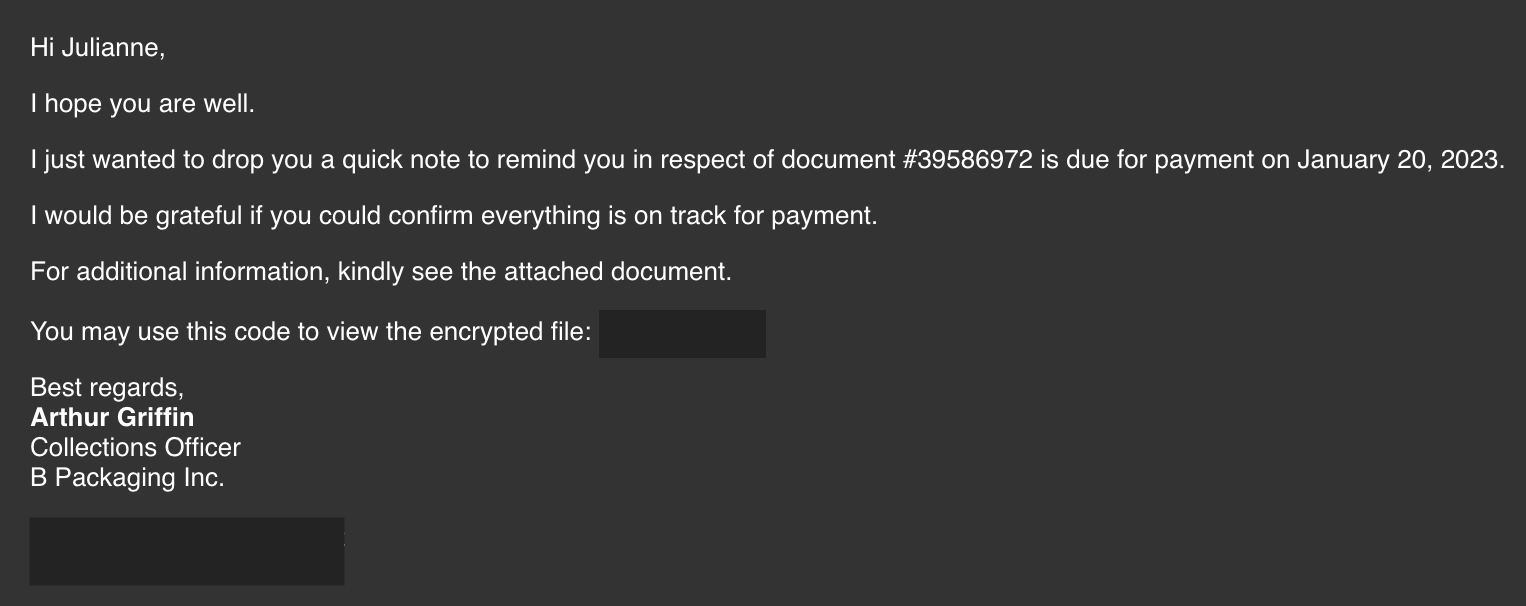
The security team was able to flag the suspicious execution of the attachment, in addition to the phishing reports received from the other finance department employees, making it seem to be a targeted attack on the finance team. Upon checking the latest trends, the initial TTP used for the malicious attachment is attributed to the new threat group named Boogeyman, known for targeting the logistics sector.
You are tasked to analyse and assess the impact of the compromise.
Investigation Guide
Given the initial information, we know that the compromise started with a phishing email. Let's start with analysing the dump.eml file located in the artefacts directory. There are two ways to analyse the headers and rebuild the attachment:
The manual way uses command-line tools such as cat, grep, base64, and sed. Analyse the contents manually and build the attachment by decoding the string located at the bottom of the file.
ubuntu@tryhackme:~
An alternative and easier way to do this is to double-click the EML file to open it via Thunderbird. The attachment can be saved and extracted accordingly.
Once the payload from the encrypted archive is extracted, use lnkparse to extract the information inside the payload.
ubuntu@tryhackme:~
Answer the questions below



What is the email address used to send the phishing email?
What is the email address of the victim?
What is the name of the third-party mail relay service used by the attacker based on the DKIM-Signature and List-Unsubscribe headers?
elasticemail
What is the name of the file inside the encrypted attachment?
Invoice_20230103.lnk
What is the password of the encrypted attachment?
Invoice2023!
Based on the result of the lnkparse tool, what is the encoded payload found in the Command Line Arguments field?
[Endpoint Security] Are you sure that’s an invoice?
Based on the initial findings, we discovered how the malicious attachment compromised Julianne's workstation:
A PowerShell command was executed.
Decoding the payload reveals the starting point of endpoint activities.
Investigation Guide
With the following discoveries, we should now proceed with analysing the PowerShell logs to uncover the potential impact of the attack:
Using the previous findings, we can start our analysis by searching the execution of the initial payload in the PowerShell logs.
Since the given data is JSON, we can parse it in CLI using the
jqcommand.Note that some logs are redundant and do not contain any critical information; hence can be ignored.
JQ Cheatsheet
jq is a lightweight and flexible command-line JSON processor**.** This tool can be used in conjunction with other text-processing commands.
You may use the following table as a guide in parsing the logs in this task.
Note: You must be familiar with the existing fields in a single log.
Parse all JSON into beautified output
cat powershell.json | jq
Print all values from a specific field without printing the field
cat powershell.json | jq '.Field1'
Print all values from a specific field
cat powershell.json | jq '{Field1}'
Print values from multiple fields
cat powershell.json | jq '{Field1, Field2}'
Sort logs based on their Timestamp
cat powershell.json | jq -s -c 'sort_by(.Timestamp) | .[]'
Sort logs based on their Timestamp and print multiple field values
cat powershell.json | jq -s -c 'sort_by(.Timestamp) | .[] | {Field}'
You may continue learning this tool via its documentation.
Answer the questions below
What are the domains used by the attacker for file hosting and C2? Provide the domains in alphabetical order. (e.g. a.domain.com,b.domain.com)
cdn.bpakcaging.xyz,files.bpakcaging.xyz
What is the name of the enumeration tool downloaded by the attacker?
The attacker mistakenly executed the exact tool name.
Seatbelt
What is the file accessed by the attacker using the downloaded sq3.exe binary? Provide the full file path with escaped backslashes.
Trace back the executed cd commands.
What is the software that uses the file in Q3?
Microsoft Sticky Notes
What is the name of the exfiltrated file?
protected_data.kdbx
What type of file uses the .kdbx file extension?
KeePass
What is the encoding used during the exfiltration attempt of the sensitive file?
hex
What is the tool used for exfiltration?
nslookup
[Network Traffic Analysis] They got us. Call the bank immediately!
Based on the PowerShell logs investigation, we have seen the full impact of the attack:
The threat actor was able to read and exfiltrate two potentially sensitive files.
The domains and ports used for the network activity were discovered, including the tool used by the threat actor for exfiltration.
Investigation Guide
Finally, we can complete the investigation by understanding the network traffic caused by the attack:
Utilise the domains and ports discovered from the previous task.
All commands executed by the attacker and all command outputs were logged and stored in the packet capture.
Follow the streams of the notable commands discovered from PowerShell logs.
Based on the PowerShell logs, we can retrieve the contents of the exfiltrated data by understanding how it was encoded and extracted.
Answer the questions below
What software is used by the attacker to host its presumed file/payload server?
Review the headers of the HTTP requests going to the server hosting malicious files used by the attacker.
python
What HTTP method is used by the C2 for the output of the commands executed by the attacker?
Using the known bad domains, find the C2 traffic and follow the streams.
POST
What is the protocol used during the exfiltration activity?

DNS
What is the password of the exfiltrated file?
The password is stored in the database file accessed by the attacker using the sq3.exe binary.
%p9^3!lL^Mz47E2GaT^y
What is the credit card number stored inside the exfiltrated file?
Retrieve the exfiltrated file first using Tshark and focus on the query type used shown in the PowerShell logs.



4024007128269551
[[Warzone 2]]
Last updated